1st July 2023


1st July 2023



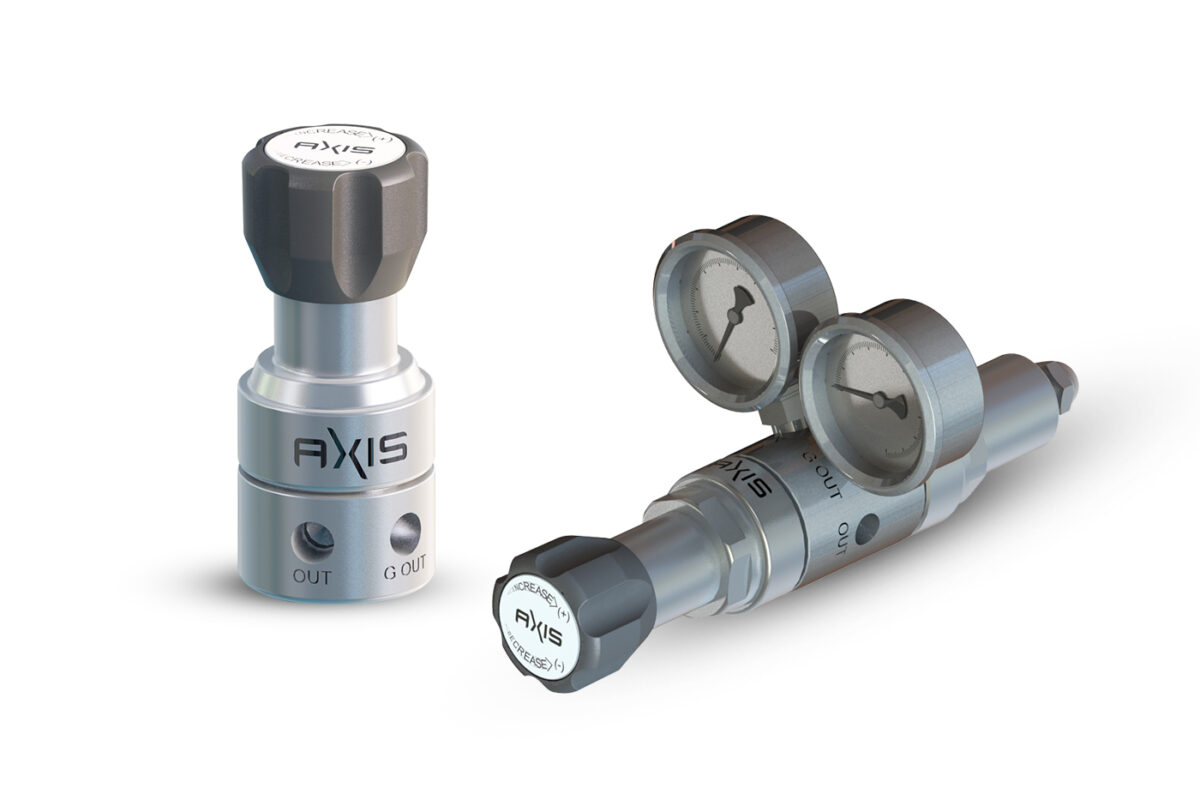
When it comes to controlling gas pressure in a laboratory or industrial setting, precision gas pressure regulators are essential. These regulators are designed to provide a constant and accurate gas flow rate, which is crucial for maintaining consistent and reliable results in analytical and manufacturing processes.
There are two main types of precision gas pressure regulators: single-stage and dual-stage. In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between these two types of regulators and when each is most appropriate to use. , we’ll take a closer look at the working principle, main components, applications, industries, advantages, and limitations of single-stage and dual-stage pressure regulators.
Single-stage regulators are the most basic type of gas pressure regulator. The reduction in pressure occurs in a single step, which is why they are called “single-stage” regulators.
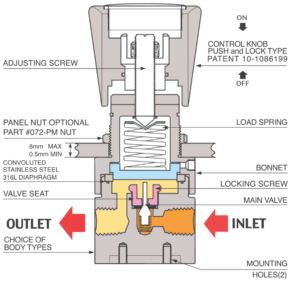
Single-stage pressure regulators work by reducing the high-pressure gas from a cylinder or supply line down to a lower, more usable pressure. The regulator consists of a valve and a diaphragm. The valve controls the gas flow rate, while the diaphragm controls the pressure.
When the gas pressure is higher than the desired output pressure, the diaphragm is pushed upwards, which closes the valve and reduces the gas flow rate. Conversely, when the gas pressure is lower than the desired output pressure, the diaphragm is pushed downwards, which opens the valve and increases the gas flow rate.

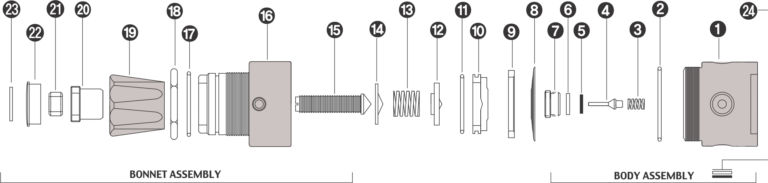
The main components of a single-stage pressure regulator include a body, diaphragm, valve, pressure gauge, and inlet and outlet connections. The body of the regulator houses the diaphragm and valve, while the pressure gauge indicates the output pressure.
Single-stage pressure regulators are commonly used in a variety of applications, including gas welding and cutting, laboratory research, chemical processing, and semiconductor manufacturing. They are also used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, energy, and medical.
Single-stage pressure regulators are relatively inexpensive and simple to use. They are suitable for applications where a consistent gas flow rate is required and are effective at reducing high-pressure gas down to a lower, more usable pressure.
Single-stage pressure regulators may not be suitable for applications where the gas supply pressure is unstable or where precise gas flow control is necessary. They are also not recommended for applications that require very low or very high output pressures.
Dual-stage regulators are more complex than single-stage regulators and provide greater precision in gas pressure control.
Dual-stage pressure regulators work by reducing the high-pressure gas from a cylinder or supply line down to a lower, more usable pressure in two stages. The first stage reduces the gas pressure from the source to an intermediate pressure, while the second stage further reduces the gas pressure to the desired output pressure.
The first stage of the regulator reduces the high-pressure gas to an intermediate pressure and maintains a relatively constant output pressure, regardless of changes in the supply pressure. The second stage further reduces the gas pressure and provides fine control over the output pressure.

The main components of a dual-stage pressure regulator include a body, diaphragms, valves, pressure gauges, and inlet and outlet connections. The body of the regulator houses the diaphragms and valves, while the pressure gauges indicate the intermediate and output pressures.
Dual-stage pressure regulators are commonly used in applications where precise gas flow control is necessary, such as in gas chromatography, analyzers, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and semiconductor manufacturing. They are also used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, energy, and medical.
Dual-stage pressure regulators offer greater precision and stability in gas pressure control than single-stage regulators. They are more suitable for applications where the gas supply pressure is unstable or where precise gas flow control is necessary. They also provide a more stable and accurate gas flow rate, which is important for critical applications.
Dual-stage pressure regulators are more expensive than single-stage regulators and may be more complex to operate. They may also not be suitable for applications where a consistent gas flow rate is required, as they are designed to provide precise control over the gas flow rate.
Single-stage pressure regulators are a popular and cost-effective option for controlling gas pressure in a variety of applications and industries. They work by reducing high-pressure gas down to a lower, more usable pressure, and consist of a valve and diaphragm. While they are suitable for many applications, they may not be appropriate for those requiring precise gas flow control or very low or very high output pressures.
Dual-stage pressure regulators are a popular option for controlling gas pressure in a variety of applications and industries that require precise gas flow control. They work by reducing the high-pressure gas down to a lower, more usable pressure in two stages and consist of multiple diaphragms and valves. While they are more expensive and complex to operate than single-stage regulators, they offer greater precision and stability in gas pressure control.
Both single-stage and dual-stage precision gas pressure regulators have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which to use depends on the specific application. Single-stage regulators are suitable for applications where consistent gas flow is required, while dual-stage regulators are preferred for applications where precise gas flow control is necessary.
It is essential to choose the right precision gas pressure regulator for your specific application to ensure accurate and reliable gas flow control. Consult with a gas pressure regulator expert to help determine which type of regulator is best suited for your application.
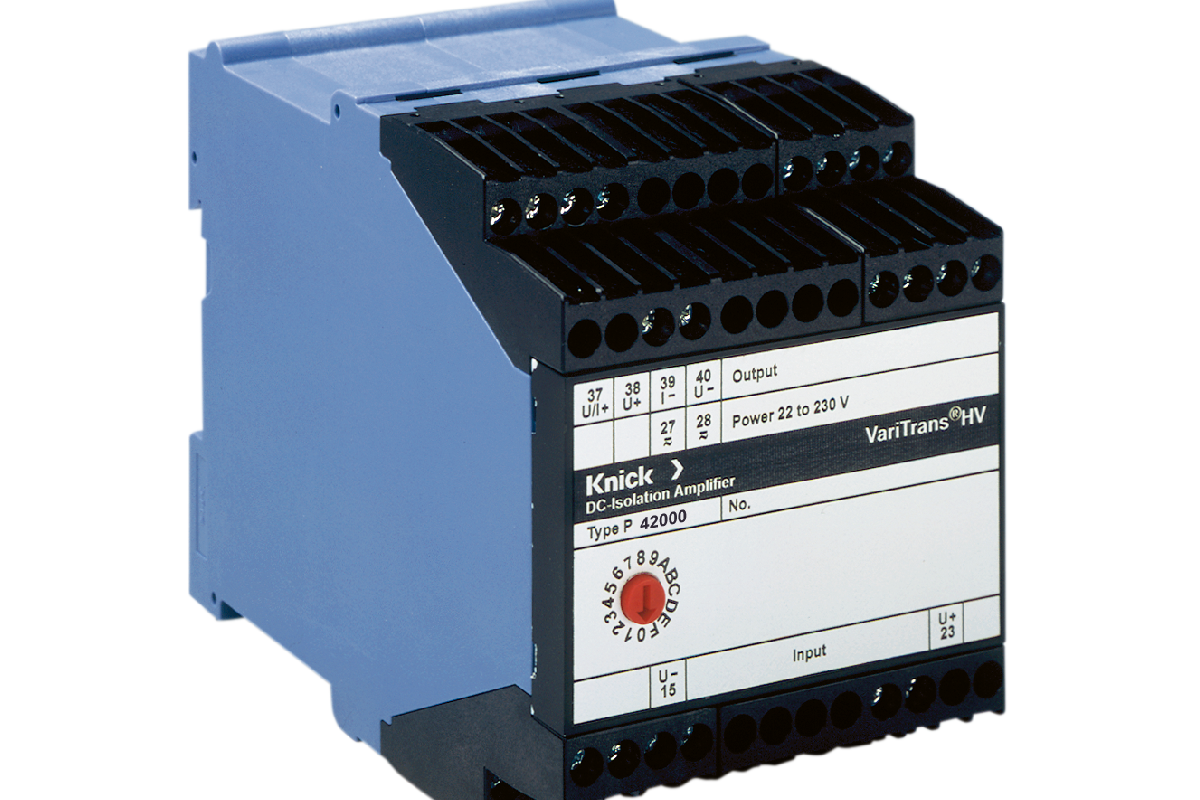
Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers are essential devices used in industries that require measurement of high voltage. These transducers are designed to measure voltage levels ranging from ±100 V to ±3600 V AC/DC with a high degree of accuracy and reliability. In this article, we will discuss the working principle, features, advantages, applications, and industries where Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers are commonly used.
Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers work based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The transducer consists of a primary winding and a secondary winding that are separated by an insulating material. When a high voltage is applied to the primary winding, it generates an electromagnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding proportional to the primary voltage. The output of the secondary winding is then amplified and converted into a standard signal, which can be used for measurement or control purposes.
Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers are known for their robust construction, high accuracy, and reliability. Some of the key features of these transducers are:
Wide voltage range: Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers can measure voltages ranging from ±100 V to ±3600 V AC/DC.
Compact design: Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers are designed to be compact and easy to install.
Low power consumption: These transducers have low power consumption, making them energy-efficient.
Isolation: The transducers provide galvanic isolation between the input and output signals, ensuring safe and accurate measurements.
Advantages: Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers offer several advantages over traditional voltage measurement methods. Some of these advantages are:
High accuracy: These transducers provide accurate voltage measurements with a high degree of precision.
Safety: The galvanic isolation provided by these transducers ensures safe voltage measurements, preventing electrical shocks and other hazards.
Durability: Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers are designed to be robust and long-lasting, making them suitable for use in harsh industrial environments.
Versatility: These transducers can measure both AC and DC voltages, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers find applications in various industries where high voltage measurements are required. Some of the common applications of these transducers are:
Power generation: Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers are used in power generation plants to measure voltage levels in transformers, generators, and other equipment.
Automotive: These transducers are used in automotive applications to measure high voltage levels in electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles.
Aerospace: Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers find applications in the aerospace industry for measuring high voltage levels in electrical systems of aircraft and spacecraft.
Industrial automation: These transducers are used in industrial automation applications for controlling and monitoring high voltage equipment.
Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers find applications in various industries, including:
Knick’s VariTrans high voltage transducers are essential devices used in industries that require measurement of high voltage. These transducers provide accurate and reliable voltage measurements, ensuring safe and efficient operation of high voltage equipment. With their robust construction, high accuracy, and versatility, these transducers are widely used in various industries, including power generation, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
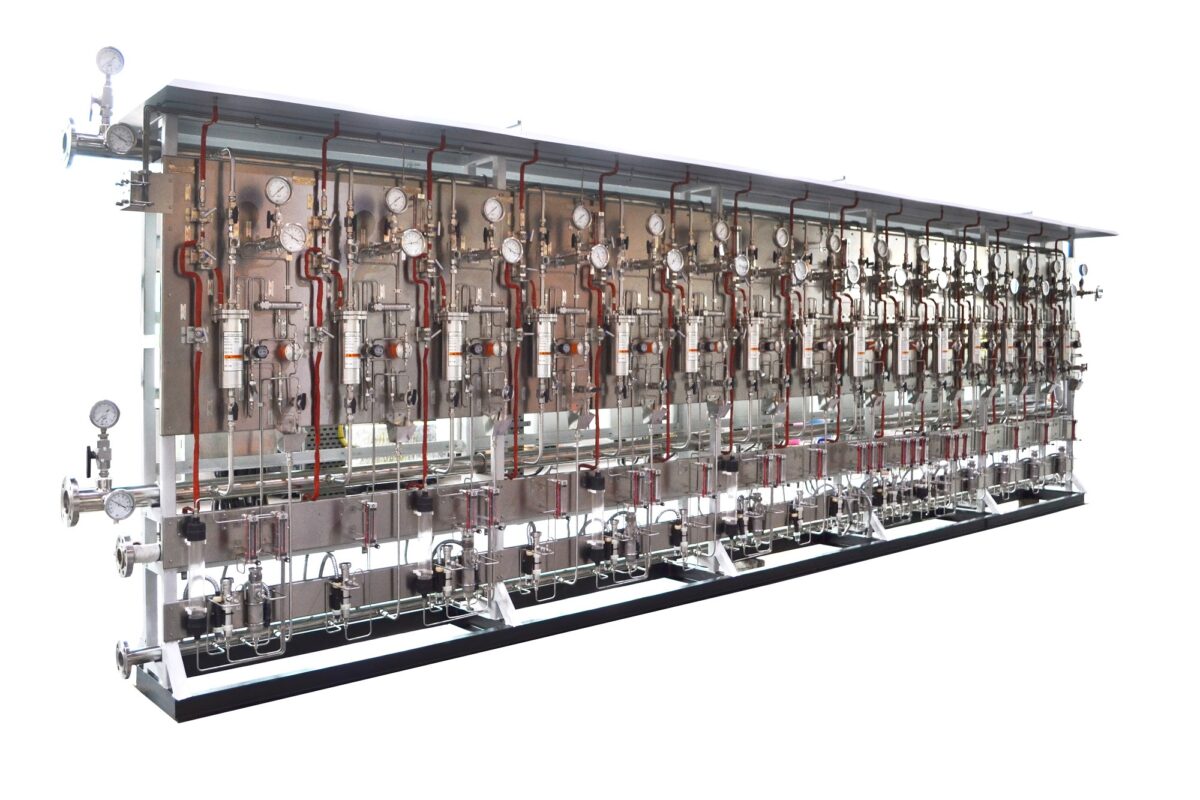
 Steam and Water Analysis System (SWAS)
Steam and Water Analysis System (SWAS)Steam and Water Analysis System (SWAS) is an essential system used in various industries to monitor and control the quality of steam and water used in various processes. SWAS is a complete analytical system that is designed to measure and analyze the quality of steam and water at various stages of the process. It consists of several analytical instruments such as conductivity meters, pH meters, dissolved oxygen analyzers, and silica analyzers.
Steam can be as hot as 560°C. Pressures can be as high as 250 bar. Samples are at high temperature & pressure. Sample conditioning is required to bring down the temperature & pressure at the desired level. To keep the power plant up and running with minimum erosion and corrosion of the steam turbine, steam boiler, and condenser, SWAS provides exact, precise measurements on all these critical parameters.
SWAS is widely used in industries such as power generation, chemical and petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage. The main purpose of using SWAS is to ensure that the quality of steam and water used in the process is within the required parameters. Poor quality steam and water can lead to corrosion, scaling, and other problems that can affect the efficiency of the process and cause equipment failure.
One of the key components of SWAS is the Conductivity meter. It measures the conductivity of water and steam, which is an indication of the total dissolved solids (TDS) in the sample. The TDS level in the water and steam is a critical parameter that needs to be monitored to ensure that it is within the required limits. High levels of TDS can lead to scaling and corrosion, which can cause damage to the equipment and reduce the efficiency of the process.
Another critical parameter that needs to be monitored is the pH level. The pH level of water and steam is an indication of its acidity or alkalinity. The pH level needs to be within the required range to prevent corrosion and scaling. The dissolved oxygen analyzer is another critical instrument used in SWAS. It measures the level of dissolved oxygen in water and steam. High levels of dissolved oxygen can cause corrosion, which can lead to equipment failure.
The Silica analyzer is another essential instrument used in SWAS. It measures the level of silica in water and steam. Silica can cause scaling, which can lead to reduced efficiency and equipment failure. The presence of silica can also cause problems in the treatment of wastewater.
SWAS have mainly two parts of system, Wet Panel and Dry Panel. In Wet Panel, Samples coming from different points are fed to this panel and it has contain all the components like Thermal auto shutoff valves (TSV), Pressure regulation valves (PRVs), Back pressure regulators (BPR) , gauges that indicates pressure and temperature, Sample coolers and sensors in many cases. In Dry Panel, Indicators, analyzers, Transmitters, remote signaling, interconnection to control room and DCS systems.
 Axis Solutions Private Limited, India utilize modern technologies and proven techniques to manufacture and integrate excellent Steam and Water Analysis System (SWAS). We are leading manufacturer and solutions provider of SWAS systems for critical parameters such as pH, Conductivity, Dissolved Oxygen, Silica, Sodium, Hydrazine and Phosphate etc. With expertise in sample cooler designs, Automatic High Temperature mechanical thermal shut-off valve and Effective Temperature & Pressure reduction with constant flow regulation to improve analyzer safety and reliability, we, axis solutions is the leading supplier of SWAS components and System integrator of single stream to multiple stream SWAS packages. We have space saving SWAS designs as well for compact spaces.
Axis Solutions Private Limited, India utilize modern technologies and proven techniques to manufacture and integrate excellent Steam and Water Analysis System (SWAS). We are leading manufacturer and solutions provider of SWAS systems for critical parameters such as pH, Conductivity, Dissolved Oxygen, Silica, Sodium, Hydrazine and Phosphate etc. With expertise in sample cooler designs, Automatic High Temperature mechanical thermal shut-off valve and Effective Temperature & Pressure reduction with constant flow regulation to improve analyzer safety and reliability, we, axis solutions is the leading supplier of SWAS components and System integrator of single stream to multiple stream SWAS packages. We have space saving SWAS designs as well for compact spaces.
In conclusion, SWAS is a critical system used in many industries to monitor and control the quality of steam and water used in various processes. It consists of several analytical instruments such as conductivity meters, pH meters, dissolved oxygen analyzers, and silica analyzers. The proper use of SWAS can help to prevent corrosion, scaling, and other problems that can affect the efficiency of the process and cause equipment failure.
24 & 25 February 2023 | Navi Mumbai